Rebutting the recent article in the Spirit of Jefferson on July 1, 2020
The Spirit of Jefferson published another Rockwool propaganda piece on July 1, 2020, with no apparent regard for the facts and no effort made to cite real sources. Here is our fact-based rebuttal.
120 vs. 150 Jobs
In May of 2019, Rockwool finalized a deal with the West Virginia Economic Development Authority (WVEDA). This deal was a bond lease agreement in which the WVEDA will take ownership of Rockwool’s land and property for 10 years, which means Rockwool will not need to pay property tax during that time. The WVEDA also promised Rockwool up to $150 million in loans fulfilled with state-backed bonds. When it came time to sign the agreement on the dotted line, Rockwool was willing to commit only to “120 full-time equivalent jobs.” And in another WVEDA deal, this time in November 2019 to obtain state help to pay for its water lines, Rockwool again committed only to “120 full-time equivalent jobs.” That is one-fifth less than the 150 jobs the July 1 article claims.
Good paying jobs? Depends on your math.
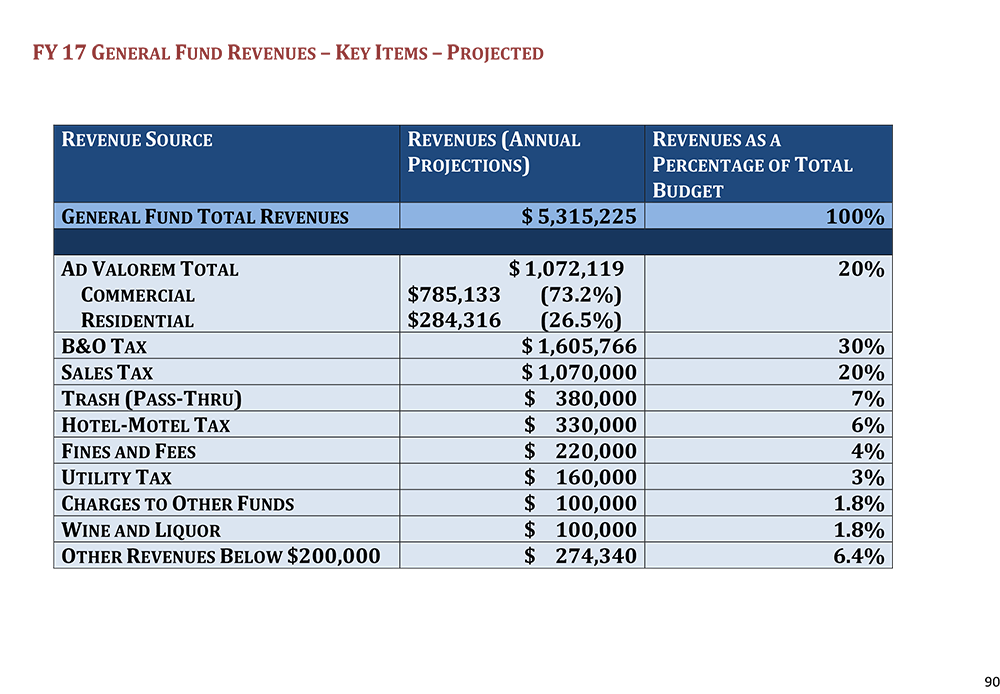
The article also repeated a claim of Espinosa, who apparently said that Rockwool would “generate” between $500,000 and $750,000 in taxes to Ranson a year. It would be very interesting to know what taxes these would be. According to Ranson’s 2017-2018 budget, the Revenue for the General Fund has three major sources: the Ad Valorem or property tax, B&O tax, and the 1% sales tax (Figure 1). With the execution of the WVEDA bond lease agreement as discussed above, Rockwool will have no property tax obligation and therefore, Ranson will collect no Ad Valorem Tax from Rockwool. The 1% sales tax is collected on retail sales and since Rockwool will have no appreciable retail sales in Ranson it therefore will not generate revenue for Ranson through the retail sales tax. B&O tax is also assessed on sales. The plant in Ranson is a manufacturing operation and Rockwool’s sales will likely be made from their headquarters in New Jersey. Therefore, Ranson is unlikely to collect any B&O tax from Rockwool either. The remainder of the taxes that round out the revenue for the Ranson General Fund are Hotel-Motel Tax, Fines and Fees, Charges to Other Funds, Garbage Service, Utility Tax, and Wine and Liquor. It is not plausible that Rockwool will be contributing significantly to any of these revenue streams. Where will this half- to three-quarters of a million dollars in tax revenue from Rockwool come from?
Paul Espinosa, public affairs manager for Rockwool Ranson and current member of the West Virginia House of Delegates (representing District 66), is cited as claiming that Rockwool’s employees will make on average $42,700 a year. This is a notable reduction from what was promised. A 2017 Deloitte economic impact study we obtained via FOIA, which was used to convince local leaders in the JCDA and elsewhere to support Rockwool, claimed the average yearly salary would be $46,611. Espinosa’s claim thus represents a surprising $3,911 per year reduction, or a more than 9% lower average pay from what was promised. Worse yet, according to the Deloitte economic impact study, paid for by Rockwool, the majority of workers (117 of them) will make an average of $31,000 a year – nowhere close to the $46,611 a year that was used to woo our public representatives.
$750,000 vs. nearly nothing
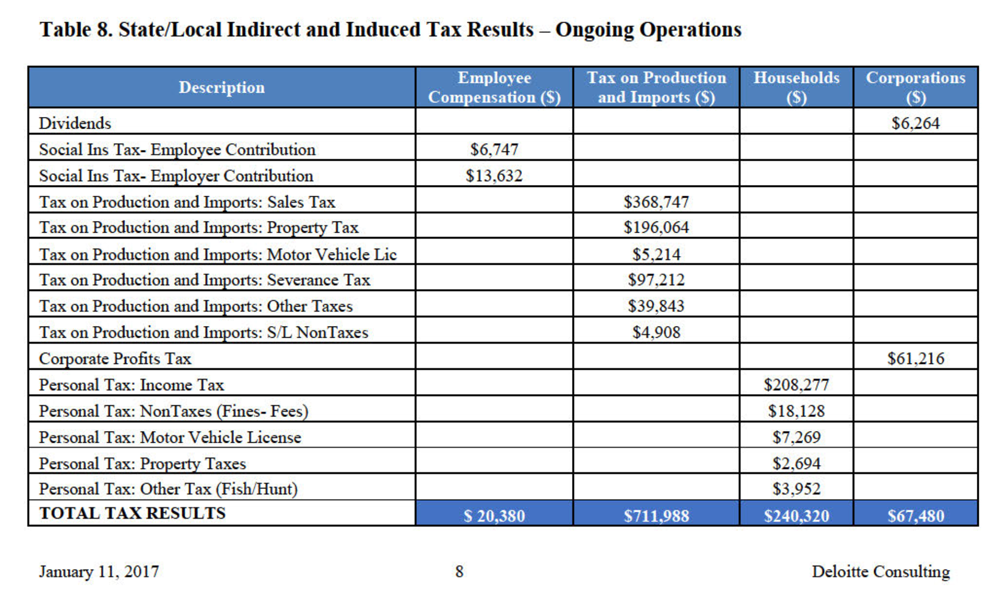
Figure 2. Source, Deloitte Economic Impact Study: Project Shuttle
It is likely that by “generate” Espinosa was slyly referring to “Indirect and Induced taxes” not taxes Rockwool will actually pay. This calculated estimated, explained in the Deloitte study, considers taxes generated by “business-to-business and household expenditure activities arising from the direct impact of Rockwool’s operations”. The issue is as explained above these business-to-business transactions will not occur in Ranson to any significant extent, because Rockwool’s suppliers are outside of Ranson. Similarly, the employees of Rockwool’s suppliers likely live nearer to those businesses and pay taxes there. Further may of the taxes taken into consideration in this calculation are state and federal not municipal taxes as can be seen in table 8.
The article also published Rockwool’s claim that for the first 10 years Rockwool will pay $40,000 in property and “other taxes.” Is Espinosa referring here to a payment in lieu of taxes? If so, we note that no payment in lieu of taxes is called for in the May 2019 WVEDA deal (which simply absolves Rockwool of their property tax burden altogether for a decade) and no other agreement providing for payments of this type can be found. And the article fails to say that only a minor portion (17%, according to the 2019 levy rate sheet) of this property tax money would go to Ranson no matter how much is paid.
Unexplained projections?
Espinosa further touts a $21.8 million yearly increase in economic activity in the county and claims that $5 million of that will be in Ranson. Frankly any rational consideration of this representation indicates it is impossible. What goods will Rockwool purchase in Ranson? There are no quarries in Ranson, no coal mines, no fracking pads, no formaldehyde concentrate dealers, no liquid oxygen suppliers – so what is Rockwool buying in Ranson to produce this $5 million impact? It is not plausible that this will all come from employee spending in Ranson. Even if every employee spent every last dollar they made after taxes and Rockwool indeed paid out $6.4 million in payroll it would not amount to $5 million in impact. This is just another in the long line of misleading and easily disproven claims to be made by Rockwool in its efforts to bring heavy industry to Jefferson County.

